BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
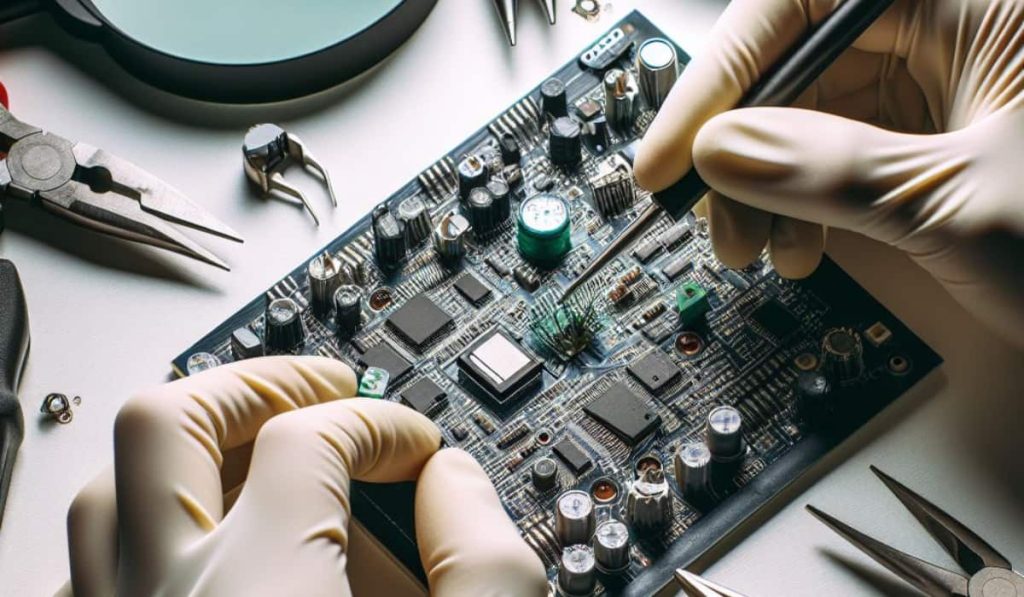
ARTICLE ADPrototype PCB assembly is the creation of an initial version of a printed circuit board design for testing and verification in electronics product development, which assesses functionality, signal integrity, and manufacturability.
In other words, prototype PCB assembly is one of the most crucial steps in electronics product development. Creating a prototype PCB brings circuit schematics to life, marking the initial physical manifestation of the design. Prototype PCB assembly encompasses this entire process.
PCB prototype assembly is the vital process of transforming electronic designs into physical boards with soldered components.
This crucial step bridges the gap between theoretical schematics and mass production, further allowing early insights and optimisations. It involves both PCB fabrication, creating physical boards from CAD designs, and assembly, soldering components based on bill of materials (BOM) requirements.
Prototyping helps mitigate risks and uncertainties in technology and manufacturing, providing a cost-effective way to validate functionality, safety, and performance before large-scale production. A good prototype assembly partner is key to the overall success of a product.
Advantages of Prototyping PCB Assembly
Exploring PCB prototypes and assemblies offers various advantages over directly engaging in mass production that are described below:
Validation of design Assurance of quality Compatibility of components Economical solutions Time-efficient processesValidation of Design
Verifies and refines the design before mass production Identifies errors and offers an opportunity for optimization Reflects the final product’s functionalityAssurance of Quality
Tests and ensures board quality and reliability Confirms compliance with specifications and standards Ensures reliable performance under different conditionsComponent Compatibility
Tests electronic components’ compatibility on the board Ensures efficient and effective collaboration of components Minimizes the risk of failure during operationEconomical Solutions
Saves costs by identifying design errors early in the process Allows necessary corrections before full-scale manufacturing Minimizes the risk of costly mistakesTime-Efficient Processes
Reduces time required for testing, validation, and production Accelerates time-to-market for the final productPrototype PCB Assembly: Why Do We Use It?
Verify Design Functionality
Examine real-world performance Testable boards validate the design and detect flaws Mitigates risks before large-scale productionAccelerate Product Development
Early verification and issue discovery Optimizes designs, saving over 60% in engineering time Significantly reduces time-to-marketFacilitate Demonstration And Funding
Showcases viability and technology capacity Builds a business case for hardware startups Attracts early adopters and investor fundingRefine Designs For Manufacturability
Reflects real-world manufacturing processes Identifies design for manufacturability (DFM) issues Ensures a smooth transition to mass productionVarieties of Prototype PCB Assembly
Various assembly methods and categories are employed to attach electronic components to PCB prototypes, addressing diverse production requirements, some of which are categorised below.
Manual Assembly vs Automated SMT Assembly Through-Hole vs SMT Assembly Single-sided vs Double-sided Assembly Hybrid Assembly TechniquesManual Assembly vs Automated SMT Assembly
Manual Assembly
Manual soldering by technicians Suitable for low-volume orders Simplest methodAutomated Assembly
Automated surface mount technology assembly Ideal for complex board productions Higher efficiency Consistency ManufacturabilityThrough-Hole vs SMT Assembly
Through-Hole Assembly (THA):
Connector pins pass through holes Respective applications Mixed THA parts on primarily SMT boards Absence of advanced features THA has a complex structureSurface-Mount Technology (SMT):
Components soldered directly onto surface pads Respective applications Advanced technology allows combining both SMT also has respective applicationsSingle-sided vs Double-sided Assembly
Single-Sided Assembly:
Components are placed and soldered on one side Suitable for less complex designsDouble-Sided Assembly:
Parts soldered on both sides, allowing higher component density Ideal for more intricate and densely populated PCBsHybrid Assembly Techniques
Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities:
Utilizes state-of-the-art manufacturing capabilities Optimizes production flexibilityComponent Mixtures on Boards:
Combines 0201 size tiny chips with larger SMT parts and some through-hole passives Allows hybrid assembly on double-sided boardsHow To Assemble A Prototype PCB
Building prototype PCBs involves following standard assembly stages to turn CAD designs into functioning boards. This can be done through automated SMT lines or manual assembly processes.
Prototype PCB Assembly Process Steps:
SMT Pick-and-Place Stage SMT Reflow Soldering Cleaning/Washing AOI and Functional Testing Final Programming/FlashingSMT Pick-and-Place Stage
Utilizes advanced pick-and-place machines for a precise component population Based on optimised programming and feeder setup Ensures high precision and traceabilitySMT Reflow Soldering
Boards pass through industrial reflow ovens after accurate component positioning. Enables simultaneous precision soldering of SMT parts Carefully optimised thermal profiling for permanent attachmentCleaning/Washing
After rework, cleaning solutions wash flux residues off board surfaces Ensures thorough removal for ionic cleanlinessAOI and Functional Testing
Automated optical inspection checks component placement Rigorous functional testing examines board performance metrics Ensures specification compliance using fixture testingFinal Programming/Flashing
Downloads optimised software/firmware builds to boards Completes prototype PCB assembly for design validation Precedes shipping to customersFinal Thoughts
Prototype PCB assembly is vital for electronics product development, verifying designs and validating concepts. Quality builds impact design optimizations and securing financing. Balancing costs, responsive turnarounds, and technical alignment are crucial. Bittele offers professional turnkey services, reshaping ideas into testable boards for commercial success. With a focus on exceptional quality and responsive support, choosing the right assembly partner is key for impactful innovation trajectories.
People Also Asked
Q: How do I make a PCB prototype?
A: The PCB prototype assembly involves the following steps:
Design Schematic creation BOM generation Routing design Thorough checksFabrication includes:
Creating photo films Printing layers Fusing Drilling Plating Applying finishesThe assembly stage includes:
Stencilling Pick and place Reflow soldering Inspection Inserting through-hole components Conducting functionality testsQ: What is a PCB prototyping machine?
A: An eco-friendly PCB machine is utilized throughout the entire PCB production process, ensuring environmentally conscious practices from design validation to board assembly.
.png)














 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·