BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE ADSamip Aryal, a cybersecurity researcher and an ethical hacker from Nepal, bypassed the system’s rate-limiting feature and subsequently checked possible combinations of 6-digit numbers (from 000000 to 999999) for two hours.
Samip Aryal, a Nepali bug bounty hunter, discovered a zero-click flaw in Facebook’s password reset system, potentially allowing hackers to compromise any targeted account. This exploit earned Aryal his highest bug bounty, making him top the Facebook Hall of Fame for White-Hat Hackers 2024 ranking, though the exact bounty amount remains unknown.]
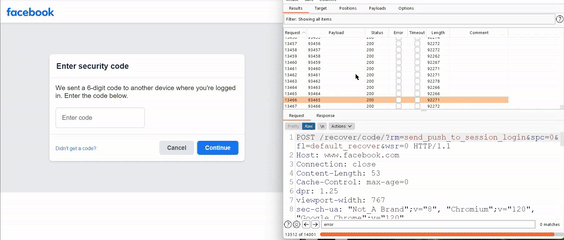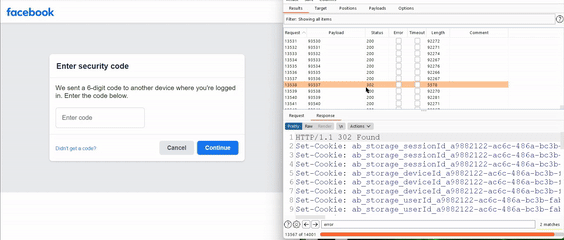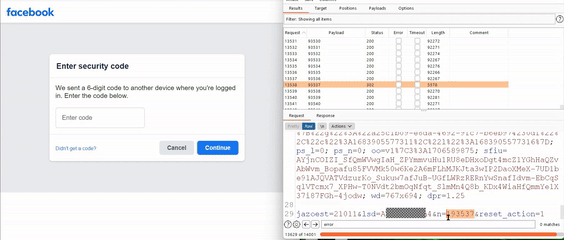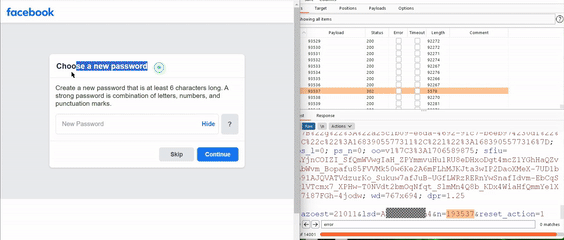
Aryal discovered a way to abuse Facebook’s password reset functionality without rate-limiting. The bug allowed attackers to hijack user accounts through “zero-click” attacks (without user interaction) by requesting a password reset and brute force the 6-digit security codes.
The vulnerability was discovered in Facebook’s password reset functionality. It allowed hackers to bypass the system’s rate-limiting feature and subsequently check possible combinations of 6-digit numbers (from 000000 to 999999) for two hours.
In his blog, Aryal revealed finding a vulnerable endpoint on Android Studio while testing Facebook versions. He received a pop-up in the password reset flow offering users to send a security code through Facebook notification. The code remained active for two hours despite incorrect inputs.
“I didn’t see any sort of code invalidation after entering the correct code but with multiple previous invalid tries (unlike in the SMS reset functionality),” Aryal explained.
He used a brute-force attack methodology to cover the entire search space in an hour, revealing that some users had the nonce code displayed on the notification, a zero-click exploit. The code was displayed on another screen with a single click.
For your information, a cryptographic nonce is an arbitrary number that can only be used once in a cryptographic communication. He further noted that hackers could hijack Facebook user accounts by choosing any account, going to its password reset flow, selecting “Send code via Facebook notification,” trying any code to receive a server response, and brute forcing it in two hours. Facebook application users would receive notifications with a six-digit code or prompting them to tap to see the login code.
Aryal responsibly disclosed the flaw to Facebook on January 30, 2024, and the issue was fixed on February 2.
The vulnerability could lead to personal information theft, disinformation spread, and network attacks. Being aware of emerging security threats on Meta and other social networking platforms is also crucial to keep your accounts protected.
It is worth mentioning that Meta accounts have particularly been the target of scams lately. In March 2023, researchers at Guardio discovered an info-stealing campaign involving fake ChatGPT extensions claiming to integrate with Google search results but in reality attempting to steal Facebook accounts.
WithSecure cybersecurity firm identified a connection between recent DarkGate malware attacks and Vietnam-based threat actors attempting to hijack Meta business accounts and steal sensitive data in October 2023.
To stay safe, users should enable two-factor authentication, use strong, unique passwords, be cautious with password reset requests, and stay updated on security threats.
.png)














 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·