BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE AD
Atlassian is prompting its enterprise customers to patch a critical vulnerability in many versions of its Jira Data Center and Jira Service Management Data Center products.
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2020-36239 can give remote attackers arbitrary code execution abilities, due to a missing authentication flaw in Jira's implementation of Ehcache, an open-source component.
Critical remote code execution due to missing authentication
Yesterday, Atlassian disclosed a critical vulnerability in its Jira Data Center products.
The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2020-36239 enables remote unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code in some Jira Data Center products.
In an email announcement seen by BleepingComputer this week, Atlassian is asking their enterprise customers to upgrade their instances ASAP as a means to fix this bug:
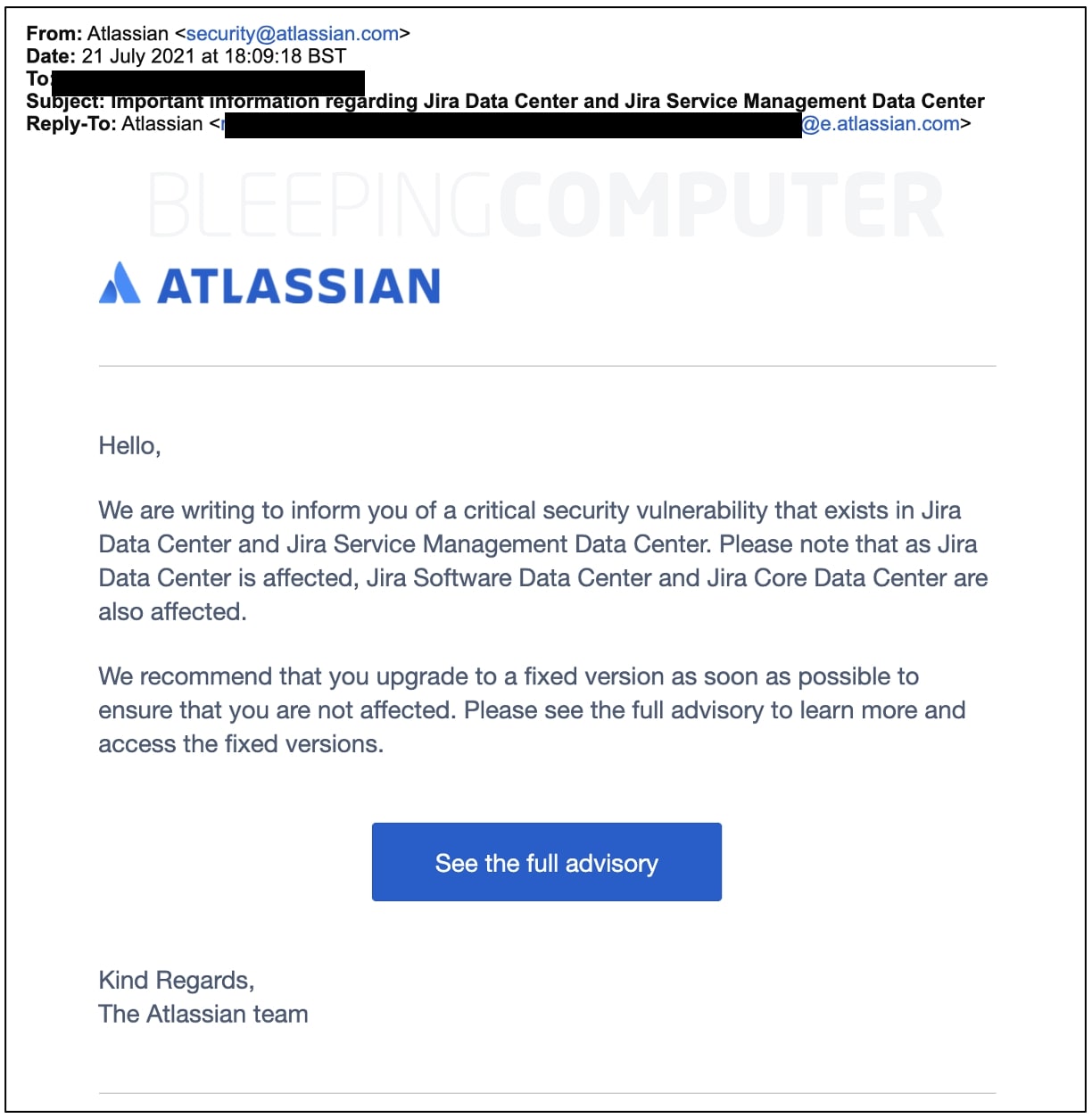 Atlassian asks customers to patch critical vulnerability (BleepingComputer)
Atlassian asks customers to patch critical vulnerability (BleepingComputer)The vulnerability stems from a missing authentication check or in other words unrestricted access to Ehcache RMI ports.
Ehcache is a widely used open-source cache used by Java applications for enhancing performance and scability.
RMI refers to remote method invocation, a concept in Java similar to remote procedure calls (RPC) in OOP languages.
RMI lets programmers invoke methods present in remote objects—such as those present within an application running on a shared network, right from their application as they would run a local method or procedure.
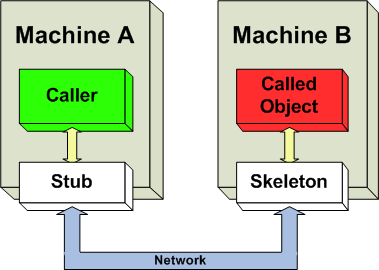 Simple Remote Method Invocation (RMI) example (Wikipedia)
Simple Remote Method Invocation (RMI) example (Wikipedia)All this is done without the programmer having to worry about implementing the underlying networking functionality, which is where RMI APIs come in handy.
In this context, multiple Jira products listed below expose an Ehcache RMI network service on ports 40001 and potentially 40011.
Remote attackers can connect to these ports without requiring any authentication, and execute arbitrary code of their choice in Jira via object deserialization.
The affected products include:
Jira Data Center Jira Core Data Center Jira Software Data Center, and Jira Service Management Data CenterThe vulnerability was discovered and responsibly reported by Harrison Neal.
Impacted versions and remediation instructions
Specifically, Jira product versions impacted by this vulnerability are:
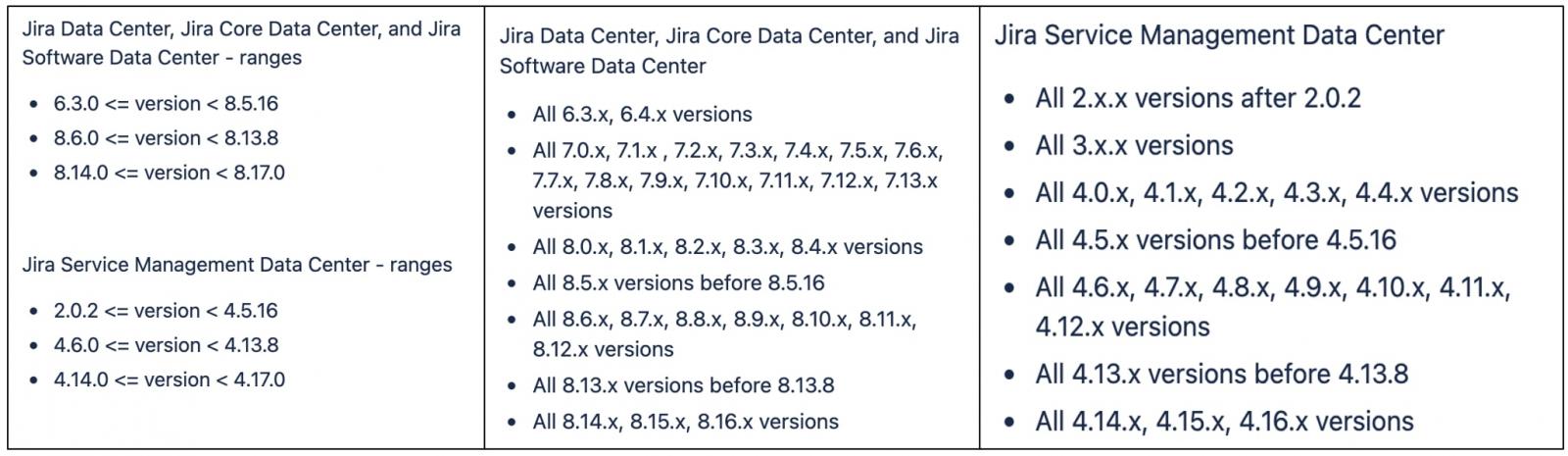 Jira products and versions affected by this bug
Jira products and versions affected by this bugFortunately, the issue does not impact non-Data Center instances of Jira Server (i.e. Core & Software), Jira Service Management, Jira Cloud, and Jira Service Management Cloud.
Jira Data Center product users should upgrade to the following versions to squash this vulnerability, depending on which version branch they are on:
Jira Data Center, Jira Core Data Center, and Jira Software Data Center users: Upgrade to 8.5.16, 8.13.8, or 8.17.0. Jira Service Management Data Center users: Upgrade to 4.5.16, 4.13.8, or 4.17.0.For those unable to upgrade their instances, Atlassian has provided workarounds in a security advisory.
Atlassian recommends that customers upgrade to the latest version of the products, and also restrict access to the Ehcache RMI ports.
Ehcache RMI ports 40001 and 40011 should be shielded using firewalls or similar technologies so that only cluster instances of Jira Data Center, Jira Core Data Center, and Jira Software Data Center, and Jira Service Management Data Center can access these.
"While Atlassian strongly suggests restricting access to the Ehcache ports to only Data Center instances, fixed versions of Jira will now require a shared secret in order to allow access to the Ehcache service," states Atlassian in a security advisory.
Thanks to Mitun Zavery for the tip-off.
.png)















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·