BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE AD
The Clop ransomware gang claims to be behind recent attacks that exploited a zero-day vulnerability in the GoAnywhere MFT secure file transfer tool, saying they stole data from over 130 organizations.
The security flaw, now tracked as CVE-2023-0669, enables attackers to gain remote code execution on unpatched GoAnywhere MFT instances with their administrative console exposed to Internet access.
Clop reached out to BleepingComputer and told us that they had allegedly stolen the data over the course of ten days after breaching servers vulnerable to exploits targeting this bug.
However, the gang refused to provide proof or share additional details regarding their claims when BleepingComputer asked them when the attacks began, if they'd already started extorting their victims, and what ransoms they were asking for.
They also claimed that they could move laterally through their victims’ networks and deploy ransomware payloads to encrypt their systems but decided against it and only stole the documents stored on the compromised GoAnywhere MFT servers.
BleepingComputer could not independently confirm Clop's claims, and Fortra has not replied to emails asking for more info regarding CVE-2023-0669 exploitation and the ransomware group's allegations.
Actively exploited flaw in secure file transfer tool
GoAnywhere MFT's developer Fortra (formerly known as HelpSystems) disclosed to its customers over the weekend that the vulnerability was being exploited as a zero-day in the wild.
On Monday, a proof-of-concept exploit was also released online, allowing unauthenticated remote code execution on vulnerable servers.
The company issued emergency security updates the next day to allow customers to secure their servers from incoming attack attempts.
Since then, Fortra has published another update on its support website (accessible only after logging in with a user account) on Thursday, saying that some of its MFTaaS instances were also breached in the attacks.
"We have determined that an unauthorized party accessed the systems via a previously unknown exploit and created unauthorized user accounts," Fortra said.
"As part of our actions to address this and out of an abundance of caution, we have implemented a temporary service outage. Service continues to be restored on a customer-by-customer basis as mitigation is applied and verified within each environment.
"We are working directly with customers to assess their individual potential impact, apply mitigations, and restore systems."
CISA also added the CVE-2023-0669 GoAnywhere MFT vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog on Friday, ordering federal agencies to patch their systems within the next three weeks, until March 3rd.
While Shodan shows that over 1,000 GoAnywhere instances are exposed online, only 135 are on ports 8000 and 8001 (the ones used by the vulnerable admin console).
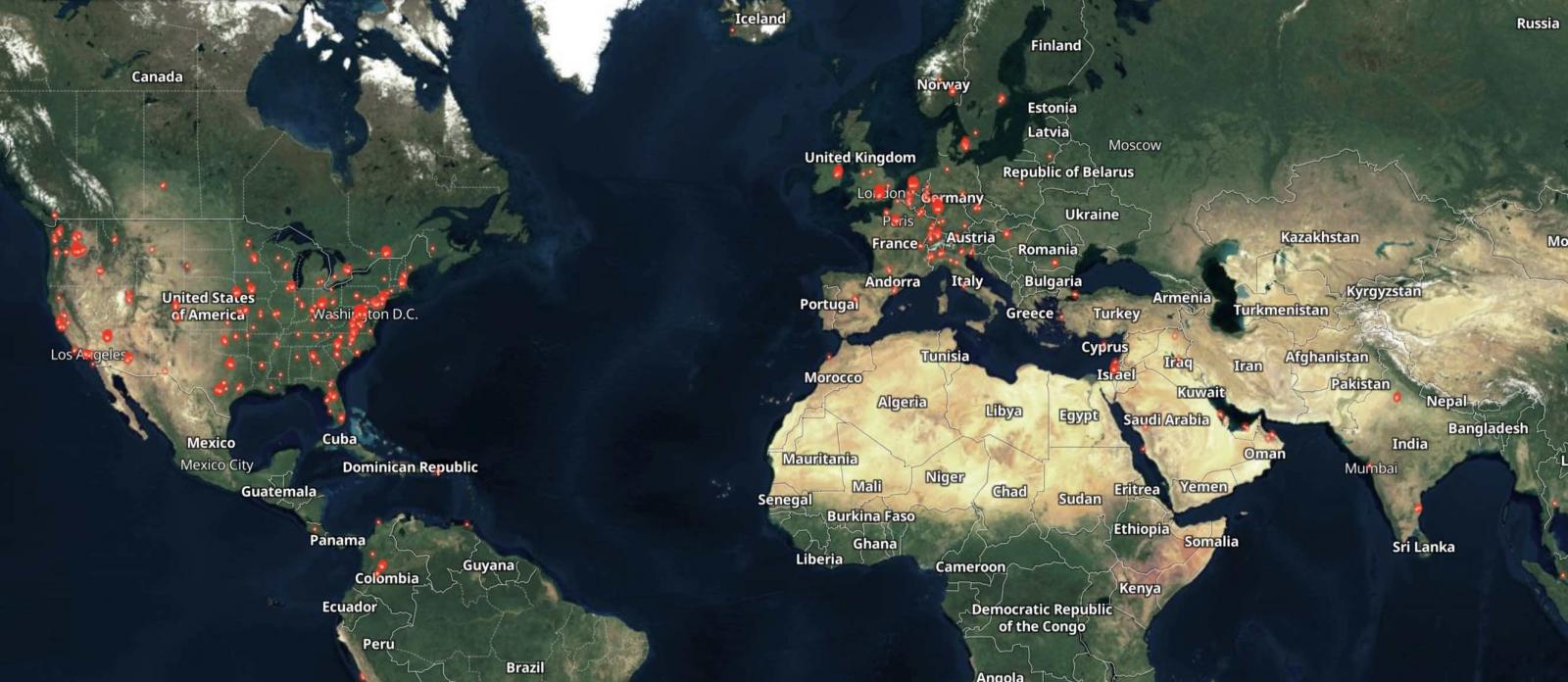 Internet-exposed GoAnywhere MFT appliances (Shodan)
Internet-exposed GoAnywhere MFT appliances (Shodan)Clop's Accellion extortion attacks
Clop's alleged use of the GoAnywhere MFT zero-day to steal data is a very similar tactic to the one they used in December 2020, when they discovered and exploited an Accellion FTA zero-day vulnerability to steal the data of approximately 100 companies.
At the time, companies were receiving emails demanding $10 million ransom payments to avoid having their data publicly leaked.
In the 2020 Accellion attacks, Clop's operators stole large amounts of data from high-profile companies using Accellion's legacy File Transfer Appliance (FTA).
Organizations that had their servers hacked by Clop include, among others, energy giant Shell, supermarket giant Kroger, cybersecurity firm Qualys, and multiple universities worldwide (e.g., Stanford Medicine, University of Colorado, University of Miami, University of Maryland Baltimore (UMB), and the University of California).
In June 2021, some of Clop's infrastructure was shut down following an international law enforcement operation codenamed Operation Cyclone when six money launderers who provided services to the Clop ransomware gang were arrested in Ukraine.
The gang has also been linked to ransomware attacks worldwide since at least 2019. Some victims that had their servers encrypted by Clop include Maastricht University, Software AG IT, ExecuPharm, and Indiabulls.
.png)















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·