BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE AD
Google Chrome now hinders attackers' efforts to exploit security bugs on systems with Intel 11th Gen or AMD Zen 3 CPUs, running Windows 10 2004 or later.
This is possible after the adoption of Intel's Control-flow Enforcement Technology (CET), supported on Windows 10 computers through an implementation known as Hardware-enforced Stack Protection which adds enhanced exploit protection to all compatible devices.
Makes it harder to write exploits
Hardware-enforced Stack Protection uses the Intel CET chipset security extension to secure applications from common exploit techniques such as Return-Oriented Programming (ROP) and Jump Oriented Programming (JOP).
Attackers regularly use such exploitation techniques to hijack a program's intended control flow to execute malicious code with the end goal of escaping a browser's sandbox or executing code remotely when visiting maliciously crafted web pages.
Windows 10's Hardware-enforced Stack Protection blocks these attacks by triggering exceptions when it detects that an app's natural flow has been modified.
"With this mitigation the processor maintains a new, protected, stack of valid return addresses (a shadow stack)," said Chrome Platform Security Team Engineer Alex Gough.
"This improves security by making exploits more difficult to write. However, it may affect stability if software that loads itself into Chrome is not compatible with the mitigation."
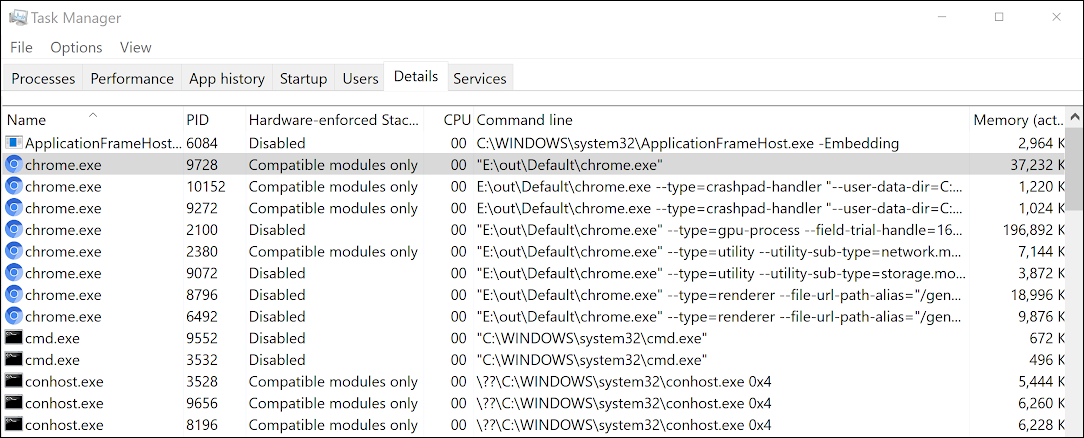 Chrome processes with Hardware-enforced Stack Protection enabled (Google)
Chrome processes with Hardware-enforced Stack Protection enabled (Google)Adopted by other Chromium-based browsers too
Google Chrome is not the first Chromium-based web browser to support Hardware-enforced Stack Protection, as BleepingComputer reported in February.
Microsoft Edge vulnerability research lead Johnathan Norman said at the time that Microsoft Edge 90 added support for the Intel CET feature in non-renderer processes.
"Edge 90 (Canary) now supports Intel's CET non-renderer processes," Norman tweeted. "If you have a fancy new processor give it a try."
This security feature will most likely be adopted by other Chromium browsers besides Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, including Brave and Opera.
Furthermore, Mozilla is also looking into including support for Intel CET in the Firefox web browser. Still, there has been no recent status update since the issue was opened one year ago.
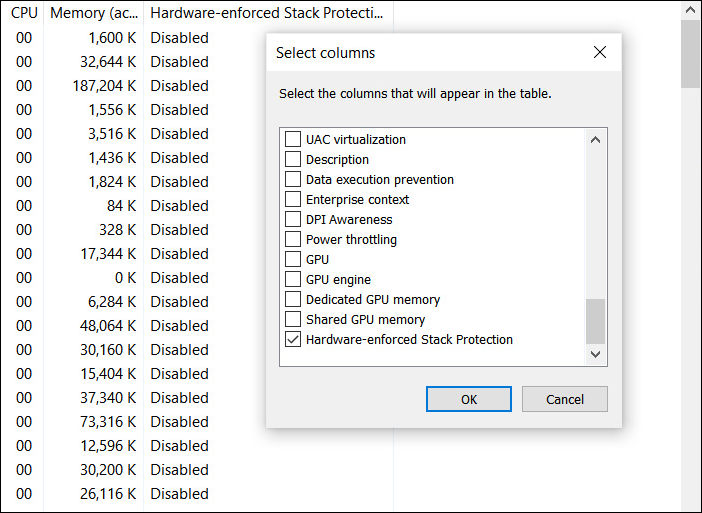 Task Manager 'Hardware-enforced Stack Protection' column
Task Manager 'Hardware-enforced Stack Protection' columnWindows 10 users with CET-compatible CPUs (Intel 11th gen or AMD Zen 3 Ryzen) can check if a browser process utilizes the hardware security feature using the Windows Task Manager.
To do this, open Task Manager, go into the Details tab, right-click on a column header, click Select Columns, and check the Hardware-enforced Stack Protection. Once enabled, a newly added column will show processes with Intel CET support.
.png)















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·