A Linux version of a multi-platform backdoor called DinodasRAT has been detected in the wild targeting China, Taiwan, Turkey, and Uzbekistan, new findings from Kaspersky reveal.
DinodasRAT, also known as XDealer, is a C++-based malware that offers the ability to harvest a wide range of sensitive data from compromised hosts.
In October 2023, Slovak cybersecurity firm ESET revealed that a governmental entity in Guyana has been targeted as part of a cyber espionage campaign dubbed Operation Jacana to deploy the Windows version of the implant.
Then last week, Trend Micro detailed a threat activity cluster it tracks as Earth Krahang and which has shifted to using DinodasRAT since 2023 in its attacks aimed at several government entities worldwide.
The use of DinodasRAT has been attributed to various China-nexus threat actors, including LuoYu, once again reflecting the tool sharing prevalent among hacking crews identified as acting on behalf of the country.
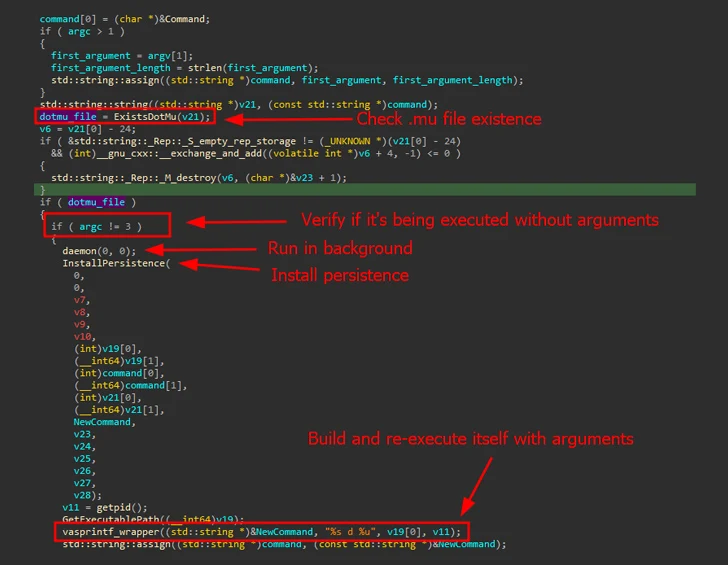
Kaspersky said it discovered a Linux version of the malware (V10) in early October 2023. Evidence gathered so far shows that the first known variant (V7) dates back to 2021.
It's mainly designed to target Red Hat-based distributions and Ubuntu Linux. Upon execution, it establishes persistence on the host by using SystemV or SystemD startup scripts and periodically contacts a remote server over TCP or UDP to fetch the commands to be run.
DinodasRAT is equipped to perform file operations, change command-and-control (C2) addresses, enumerate and terminate running processes, execute shell commands, download a new version of the backdoor, and even uninstall itself.
It also takes steps to evade detection by debugging and monitoring tools, and like its Windows counterpart, utilizes the Tiny Encryption Algorithm (TEA) to encrypt C2 communications.
"DinodasRAT's primary use case is to gain and maintain access via Linux servers rather than reconnaissance," Kaspersky said. "The backdoor is fully functional, granting the operator complete control over the infected machine, enabling data exfiltration and espionage."
Found this article interesting? Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.
.png)
 7 months ago
125
7 months ago
125 

















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·