A new set of critical vulnerabilities has been disclosed in the Realtek RTL8170C Wi-Fi module that an adversary could abuse to gain elevated privileges on a device and hijack wireless communications.
"Successful exploitation would lead to complete control of the Wi-Fi module and potential root access on the OS (such as Linux or Android) of the embedded device that uses this module," researchers from Israeli IoT security firm Vdoo said in a write-up published yesterday.
The Realtek RTL8710C Wi-Fi SoC underpins Ameba, an Arduino-compatible programmable platform equipped with peripheral interfaces for building a variety of IoT applications by devices spanning across agriculture, automotive, energy, healthcare, industrial, security, and smart home sectors.
The flaws affect all embedded and IoT devices that use the component to connect to Wi-Fi networks and would require an attacker to be on the same Wi-Fi network as the devices that use the RTL8710C module or know the network's pre-shared key (PSK), which, as the name implies, is a cryptographic secret used to authenticate wireless clients on local area networks.
The findings follow an earlier analysis in February that found similar weaknesses in the Realtek RTL8195A Wi-Fi module, chief among them being a buffer overflow vulnerability (CVE-2020-9395) that permits an attacker in the proximity of an RTL8195 module to completely take over the module without having to know the Wi-Fi network password.
In the same vein, the RTL8170C Wi-Fi module's WPA2 four-way handshake mechanism is vulnerable to two stack-based buffer overflow vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-27301 and CVE-2020-27302, CVSS scores: 8.0) that abuse the attacker's knowledge of the PSK to obtain remote code execution on WPA2 clients that use this Wi-Fi module.
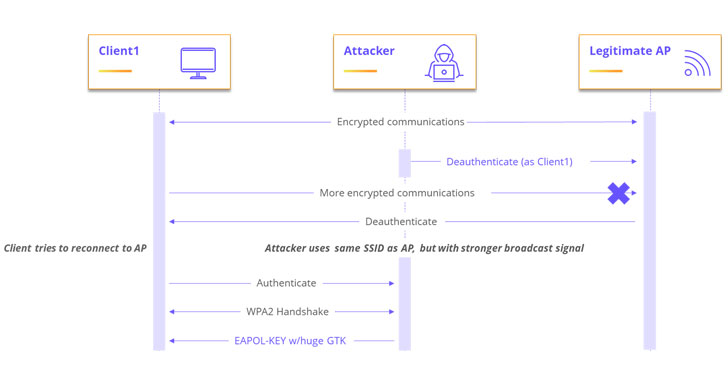
As a potential real-world attack scenario, the researchers demonstrated a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit wherein the attacker masquerades as a legitimate access point and sends a malicious encrypted group temporal key (GTK) to any client (aka supplicant) that connects to it via WPA2 protocol. A group temporal key is used to secure all multicast and broadcast traffic.
Vdoo said there are no known attacks underway exploiting the vulnerabilities, adding firmware versions released after Jan. 11, 2021 include mitigations that resolve the issue. The company also recommends using a "strong, private WPA2 passphrase" to prevent exploitation of the above issues in scenarios where the device's firmware can't be updated.
Found this article interesting? Follow THN on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.
.png)
 3 years ago
178
3 years ago
178 
















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·