BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE ADUAC-0063: A Russian-linked threat actor targeting Central Asia and Europe with sophisticated cyberespionage campaigns, including weaponized documents, data exfiltration, and advanced malware.
Bitdefender has shared its latest research with Hackread.com ahead of its release, revealing an active espionage campaign by Russia APT28-linked threat actor UAC-0063. According to Bitdefender’s investigation, the actor is specifically targeting high-value entities in Central Asia and European countries like Germany, the UK, Romania, and the Netherlands in a multi-stage attack process involving various malware components and techniques.
UAC-0063 has been active since at least 2021 and has targeted a variety of organizations, including government entities, diplomatic missions, and private companies. In this campaign, the actor employs malicious Microsoft Word documents, a HATVIBE malware loader, and custom-built malware to infiltrate networks. Their operations are characterized by persistence, focusing on maintaining long-term access to compromised systems.
The attack starts with compromised Microsoft Word documents containing malicious macros that, when enabled by the user, deliver the initial malware payload (HATVIBE loader). HATVIBE is an HTA (HTML Application) script that downloads and executes further malicious code from the attacker’s command-and-control (C2) server.
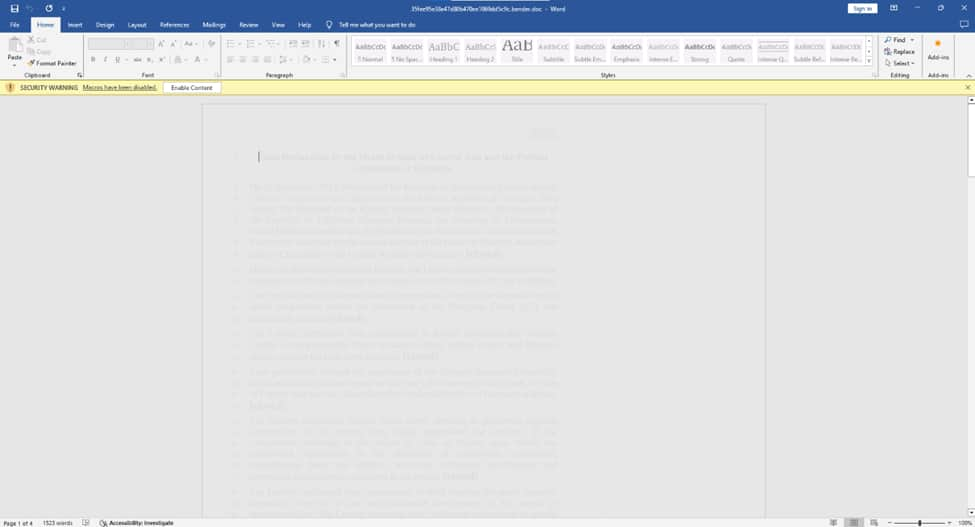 A blurred malicious MS Word document used in the attack prompts users to enable macros to reveal its contents. However, once enabled, it also allows attackers to deploy a malicious payload. (Via Bitdefender)
A blurred malicious MS Word document used in the attack prompts users to enable macros to reveal its contents. However, once enabled, it also allows attackers to deploy a malicious payload. (Via Bitdefender)DownExPyer is used extensively throughout the UAC-0063 attack chain. It is deployed after the initial infection stage, likely by the HATVIBE loader or other malware components. This Python-based malware establishes persistent communication with the C2 server, receives commands, and executes malicious actions on the infected system.
PyPlunderPlug is a separate script designed to collect files from removable drives connected to the infected system. It focuses on specific file types and copies them to a staging location for potential exfiltration.
The attackers also deploy keyloggers to capture keystrokes entered by the victim, potentially revealing sensitive information like passwords and login credentials. The stolen data is then compressed into smaller archives to facilitate exfiltration and evade detection.
Researchers noted that the actor leverages previously compromised victims to spread the infection. This means the weaponised documents exfiltrated from one victim are used to attack other targets. Moreover, they create scheduled tasks to ensure the persistence of their malware on the compromised system. These tasks automatically execute the malicious code at regular intervals.
Researchers hinted at the involvement of the Russian government in this campaign.
UAC-0063’s arsenal “featuring sophisticated implants like DownExPyer and PyPlunderPlug, combined with well-crafted TTPs, demonstrates a clear focus on espionage and intelligence gathering. The targeting of government entities within specific regions aligns with potential Russian strategic interests,” Bitdefender researchers wrote in the blog post.
To mitigate the risks posed by UAC-0063, organizations should enhance their threat intelligence by continuously monitoring feeds from reputable sources, tracking C2 domains and implementing DNS-based blocking mechanisms to prevent network traffic from reaching these malicious domains. Implementing application whitelisting policies and deploying Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) are crucial for strengthening endpoint and network security.
.png)











 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·