BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE ADThe thrilling UEFA League, aka Euro 2024, is attracting over 20 million football fans in Germany and millions more worldwide. However, this excitement has also attracted the attention of threat actors who are exploiting the event’s anticipation to fulfil their nefarious objectives.
A new report from Cyberint highlights a surge in cyber threats targeting the event. Its Dark Web monitoring reveals threat actor discussions related to UEFA, sales account searches, ticket offers, free/cheap streaming services, and the sale of compromised customer credentials.
Reportedly, threat actors are using compromised UEFA customer credentials to perform fraudulent activities, such as account takeovers and ticket purchases. They can also steal sensitive personal information, impersonate account owners, and gain access to funds or payment cards.
Cyberint has detected over 15,000 exposed UEFA customer credentials since 2024, and over 2,000 UEFA customer credentials were found for sale on dark web marketplaces. These credentials are often exposed through credential harvesting malware, which infects the victim’s machine and sends user input logs to the C&C server operator.
Since UEFA has sold streaming rights for its tournaments to media networks, it provides cybercriminals with an opportunity to create illegal content sites to lure fans without cable or streaming subscriptions through promises of free livestreaming and real-time scores. Clicking on links on these malicious websites can lead to data breaches or virus infections. These sites may demand ransom for the victim’s computer and network, or gain control of a system for fraud or spying. Drive-by downloads, a type of malware attack, can also occur by visiting the site.
Researchers noted that mobile apps impersonating UEFA’s official app are widely available on third-party app stores, often containing malicious elements. These stores are less regulated, allowing anyone to upload unauthorized apps without supervision.
Threat actors upload unauthorized apps, often containing malicious elements, exposing users to malware and data breaches. The apps target UEFA’s fans, customers, and volunteers, using the brand’s name and logo.
Moreover, Euro 2024 fans are increasingly relying on third-party ticket-selling websites, which also presents opportunities for scammers. Some sellers exploit fans’ enthusiasm by peddling fake or non-existent tickets, reaching out through social media or creating elaborate phishing websites to mimic legitimate ticket sellers.
Another fraud vector is the ticket lottery, offering fans a chance to earn free tickets. Threat actors can use the provided details to target victims for scams or sell the information to the highest bidder.
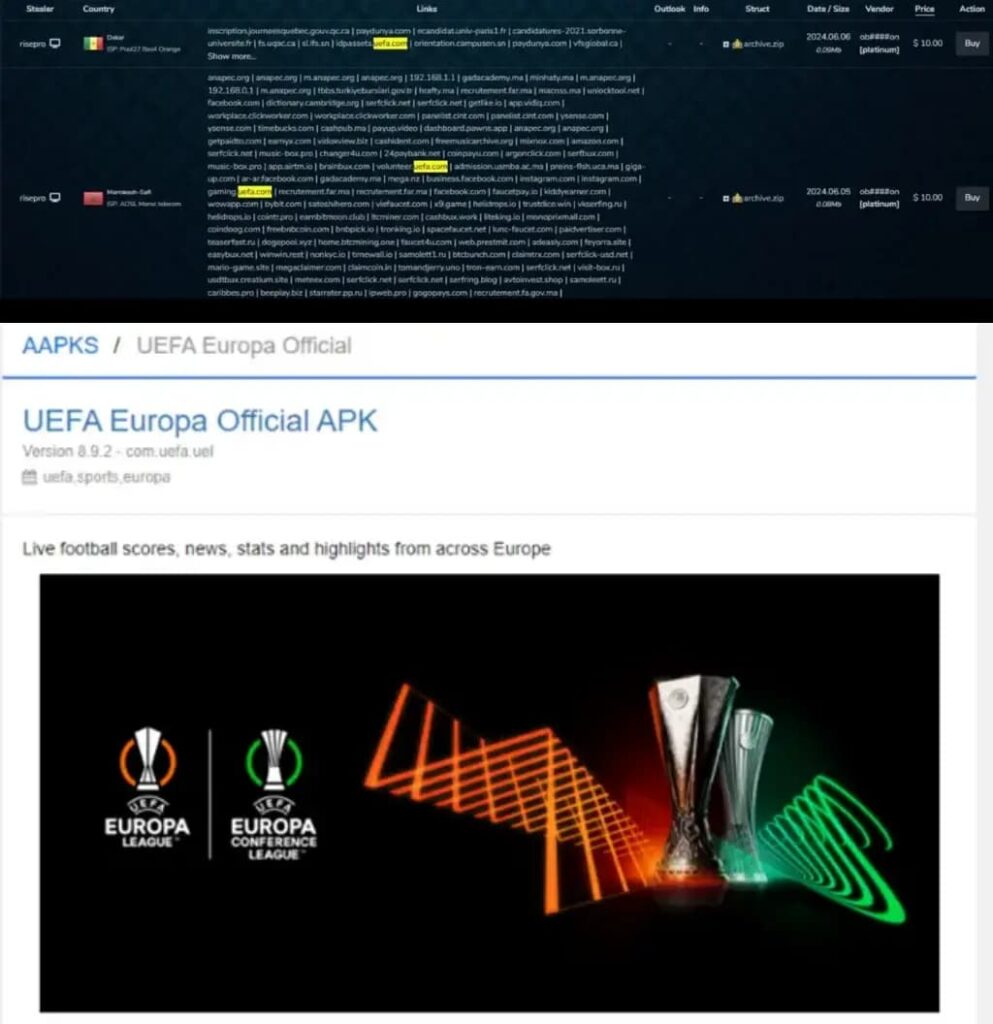 Screenshot shows cybercriminals selling UEFA customer accounts and a malicious app impersonating the original UEFA app (Screenshot: Cyberint)
Screenshot shows cybercriminals selling UEFA customer accounts and a malicious app impersonating the original UEFA app (Screenshot: Cyberint)Researchers identified that UEFA’s website might be the weak link in this scenario.
“One notable aspect is the misconfiguration of UEFA’s official website – uefa.com. Such vulnerabilities present a tangible risk, potentially serving as gateways for threat actors to launch attacks,” researchers explained in the report shared with Hackread.com.
Cyberint recommends being cautious of unsolicited communications, verifying website authenticity, and using secure payment methods. To avoid ticket fraud, buy tickets only from authorized sources, use secure payment platforms like PayPal, prefer credit card payments, and avoid direct bank or money transfers, to prevent Euro 2024 from being marred by “opportunist threat actors.”
.png)














 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·