BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE ADNew Stealer Campaign Exploits Windows SmartScreen Vulnerability (CVE-2024-21412) – This large-scale attack targets Windows users, stealing passwords, browsing history, and crypto wallet details.
FortiGuard Labs has identified a large-scale stealer campaign targeting Microsoft Windows users. This campaign exploits a known vulnerability (CVE-2024-21412) to bypass security measures and steal sensitive data.
CVE-2024-21412 is a security bypass vulnerability in Microsoft Windows SmartScreen, a feature designed to alert users to potentially unsafe applications or websites. The flaw allows remote attackers to bypass the SmartScreen security warning dialogue and deliver malicious files.
Over the past year, several attackers, including Lumma Stealer and Meduza Stealer, have exploited this vulnerability, Fortinet researchers noted.
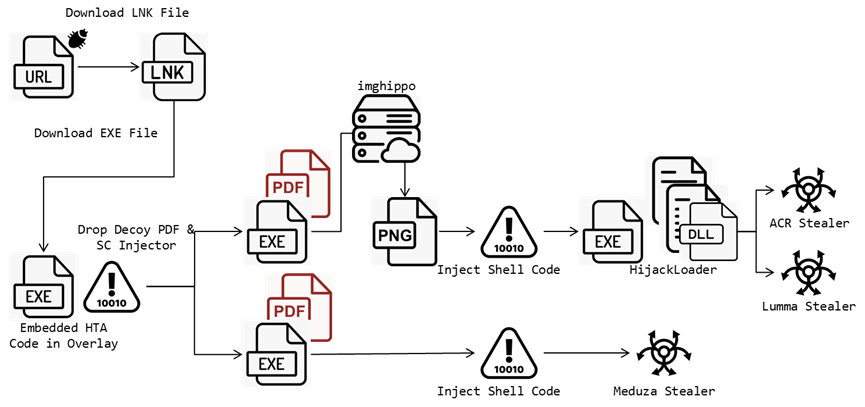
Attack Chain
This campaign, as per FortiGuard Labs’ report shared with Hackread.com ahead of publishing on Tuesday, July 23, 2024, spreads multiple files that exploit CVE-2024-21412 to download malicious executable files. Here is the sequence of attacks.
Initial Phishing: The campaign begins with a phishing email containing a malicious link. Clicking the link downloads a URL file that, in turn, downloads an LNK file. LNK File Execution: The LNK file utilizes PowerShell commands to download an HTA script disguised as an overlay icon. HTA Script Decodes Payload: The HTA script retrieves and executes a hidden PowerShell script, which runs silently and downloads a decoy PDF and a malicious shell code injector, injecting the final stealer into legitimate processes. Shellcode Injection: Two types of injectors have been identified. The first injector uses an image file to obtain a shell code, with low detection rates on VirusTotal. The second injector downloads a JPG file from the Imghippo website and uses the Windows API “GdipBitmapGetPixel” to access pixels and decode bytes to get the shell code. The other injector is more straightforward, decrypting its code from the data section and using a series of Windows API functions to perform shell code injection. Stealer Deployment: The injected code downloads and installs information-stealing malware, such as Meduza Stealer version 2.9 or ACR Stealer.Stolen Data and Regional Targeting
The ACR Stealer targets various applications, including browsers, crypto wallets, messengers, FTP clients, email clients, VPN services, password managers, and other tools. The stealer can adapt legitimate web services to maintain communications with its C2 server. The campaign seems to target specific regions, with decoy PDFs tailored to North America, Spain, and Thailand.
Implementing Microsoft’s latest security updates to address the CVE-2024-21412 vulnerability is crucial to stay protected. Users should be cautious of phishing links and downloading unknown files. Email security solutions can detect and block phishing attempts. A comprehensive security suite can provide real-time malware protection.
The full list of targeted applications is available here.
Mr. Ngoc Bui, Cybersecurity Expert at Menlo Security commented on the recent development stating,
“The recent discovery of CVE-2024-21412 reveals the persistent and evolving nature of cyber threats targeting Microsoft’s SmartScreen. It demonstrates that attackers are constantly refining their tactics to bypass traditional security measures and deliver malicious payloads to high-value targets. This highlights the need for proactive threat intelligence and layered defences to protect against these sophisticated attacks.”
.png)















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·