In the last few years, attacks on deployed smart contracts in the Ethereum blockchain have ended up in a significant amount of stolen funds due to programming mistakes. Since smart contracts, once compiled and deployed, are complex to modify and update different practitioners have suggested the importance of reviewing their security in the blockchain where only Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) bytecode is available. In this respect, reverse engineering through disassemble and decompilation can be effective.
ghidra-EVM is a Ghidra module for reverse engineering smart contracts. It can be used to download Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) bytecode from the Ethereum blockchain and disassemble and decompile the smart contract. Further, it can analyze creation code, find contract methods and locate insecure instructions.
It comprises a processor module, custom loader and plugin(s) that disassembles Ethereum VM (EVM) bytecode and generates a control-flow graph (CFG) of a smart contract.
The last version uses the Ghidra 9.1.2 API. It relies on the crytic evm_cfg_builder library (https://github.com/crytic/evm_cfg_builder) to assist Ghidra in the CFG generation process.
Ghidra-evm consists of:
A loader that reads byte and hex code from .evm and .evm_h files respectively (See examples). The SLEIGH definition of the EVM instruction set taking into account the Ghidra core limitations (See Notes). A helper script that uses evm_cfg_builder and ghidra_bridge in order to assist ghidra generating the CFG and exploring the function properties of a smart contract. A collection of scripts that help to reverse engineering different aspects of a smart contract:| search_codecopy.py | When analyzing creation code in a smart contract we can only see the _dispatcher function that uses CODECOPY in order to write the run time code into memory. This script looks for useful CODECOPY instructions and finds the smart contract methods hidden in the runtime part of the contract. |
| search_dangerous_instructions.py | Instructions such as CALL, CALLCODE, SELFDESTRUCT and DELEGATECALL can sometimed be abused to transfer funds to another contract. This script finds them and creates a label for each occurrence. |
| load_external_contract.py | Downloads smart contract byte code from the blockchain into a .evm_h file that can be loaded into ghidra-evm |
Installation instructions
Install ghidra_bridge, following the instructions at https://github.com/justfoxing/ghidra_bridge Install the crytic evm_cfg_builder library, following the instructions at https://github.com/crytic/evm_cfg_builder Install the last ghidra-evm release file at ghidra_evm/dist/: Open ghidra File -> Install Extensions Click on '+' and select the zip file e.g. ghidra_9.1.2_PUBLIC_20201102_ghidra_evm.zip Click OK Restart GhidraCompilation instructions
The contents of the ghidra-evm directory can be used to create a Ghidra module in Eclipse with processor and loader in order to extend or debug ghidra_evm.
Tutorials
Integration with external symbolic execution tools
| teether | It marks the critical path in Ghidra before generating the exploit. Requires teether. |
Notes
The CFG is created according to evm_cfg_builder: JUMP and JUMPI instructions are utilized. A jump table of 32x32 (evm_jump_table) is generated accordingly in order to detect and show branches in the disassembly and control flow windows. Ghidra has not been designed to deal with architectures and memories of wordsize > 64-bit. This means that instructions such as PUSH32 are not correctly shown in the decompilation window.License
Ghidra-evm is licensed and distributed under the AGPLv3.
Thanks
This work was supported by the European Commission through the H2020 Programme’s Project M-Sec under Grant 814917.
.png)
 3 years ago
186
3 years ago
186 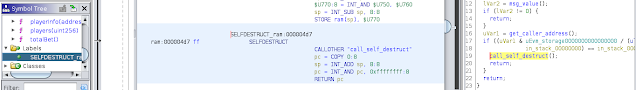

















 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·