BOOK THIS SPACE FOR AD
ARTICLE AD
Threat actors are now actively scanning for the Microsoft Exchange ProxyShell remote code execution vulnerabilities after technical details were released at the Black Hat conference.
Before we get to the active scanning of these vulnerabilities, it is important to understand how they have been disclosed.
ProxyShell is the name for three vulnerabilities that perform unauthenticated, remote code execution on Microsoft Exchange servers when chained together.
These chained vulnerabilities are exploited remotely through Microsoft Exchange's Client Access Service (CAS) running on port 443 in IIS.
The three chained vulnerabilities used in ProxyShell attacks are:
CVE-2021-34473 - Pre-auth Path Confusion leads to ACL Bypass (Patched in April) CVE-2021-34523 - Elevation of Privilege on Exchange PowerShell Backend (Patched in April) CVE-2021-31207 - Post-auth Arbitrary-File-Write leads to RCE (Patched in May)Strangely, while both CVE-2021-34473 and CVE-2021-34523 were first disclosed in July, they were actually quietly patched in April's Microsoft Exchange KB5001779 cumulative update.
The vulnerabilities were discovered by Devcore Principal Security Researcher Orange Tsai, whose team received a $200,000 prize for their use in April's Pwn2Own 2021 hacking contest.
On Thursday, Orange Tsai gave a Black Hat talk about recent Microsoft Exchange vulnerabilities he discovered when targeting the Microsoft Exchange Client Access Service (CAS) attack surface.
As part of the talk, Tsai explained that one of the components of the ProxyShell attack chain targets the Microsoft Exchange Autodiscover service.
Microsoft introduced the Autodiscover service to provide an easy way for mail client software to auto-configure itself with minimal input from the user.
 Slide from Orange Tsai's talk showing the Autodiscover URL
Slide from Orange Tsai's talk showing the Autodiscover URLAfter watching Orange Tsai's talk, security researchers PeterJson and Jang published an article providing technical information about how they could successfully reproduce the ProxyShell exploit.
Attackers scan for vulnerable Exchange servers
This week, security researcher Kevin Beaumont tweeted that a threat actor was probing his Microsoft Exchange honeypot against the server's Autodiscover service.
Interesting thing I noticed in MailPot with Exchange servers - somebody has started targeting them using autodiscover.json, a detection avoidance and relatively undocumented feature it appears. pic.twitter.com/MOuTaoOQL2
— Kevin Beaumont (@GossiTheDog) August 2, 2021While these initial attempts were unsuccessful, last night, after more details about the vulnerability were released, attackers modified their scans to use the new Autodiscover URL disclosed in Tsai's slide above.
https://Exchange-server/autodiscover/autodiscover.json?@foo.com/mapi/nspi/?&Email=autodiscover/autodiscover.json%3F@foo.comUsing the new URL, it appears that the threat actors were successfully able to detect a vulnerable system as it triggers the compilation of the ASP.NET web application.
Jang told BleepingComputer that accessing the URL will cause the ASP.NET worker process (w3wp.exe exe) to compile a web application, as shown in the image below from Beaumont's honeypot.
Now that threat actors are actively scanning for vulnerable Microsoft Exchange servers, Beaumont advises administrators to use Azure Sentinel to check IIS logs for the "/autodiscover/autodiscover.json" or "/mapi/nspi/" strings.
W3CIISLog | where csUriStem == "/autodiscover/autodiscover.json" | where csUriQuery has "/mapi/nspi/"If the results list the targeted Autodiscover URL, then threat actors scanned your server for the vulnerability.
Threat actors are actively trying to exploit this vulnerability, with little success so far. However, it is only a matter of time until successful exploitation is achieved in the wild.
It is strongly advised that Microsoft Exchange admins install the latest cumulative updates so they are protected from these vulnerabilities
CVE-2021–34473 is one announced last month (but patch available in April). However, about 50% of internet exposed boxes aren't patched yet.
— Kevin Beaumont (@GossiTheDog) August 7, 2021BleepingComputer has contacted Microsoft about this activity but has not heard back at this time.
.png)
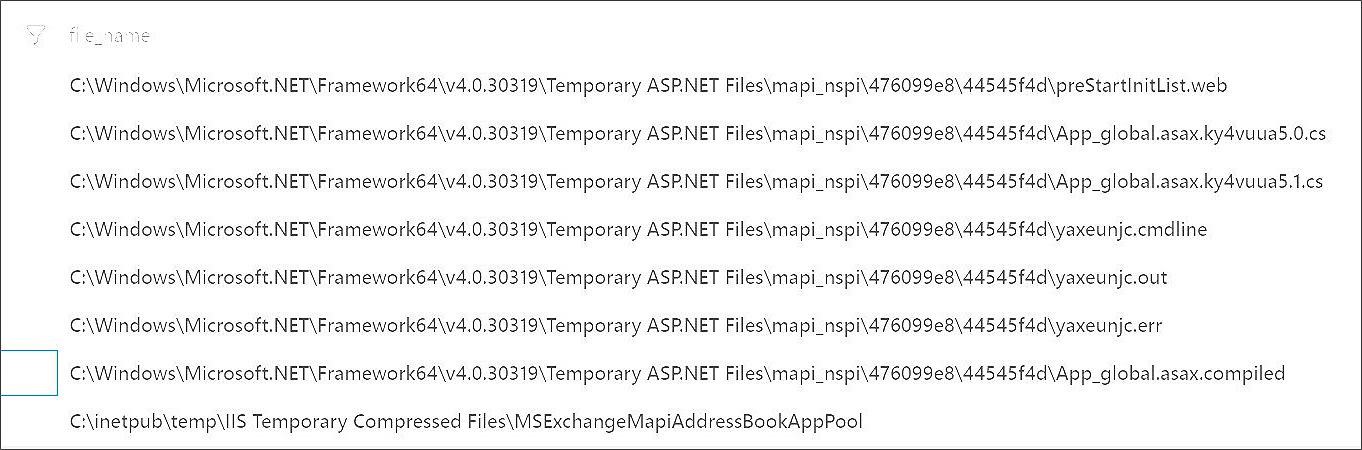 Files created by the scan on Microsoft Exchange honeypot
Files created by the scan on Microsoft Exchange honeypot














 Bengali (Bangladesh) ·
Bengali (Bangladesh) ·  English (United States) ·
English (United States) ·